|
Circuit Solutions Notebook
Last Updated On:
Wednesday June 02, 2021
|
|
|
|
Latest Technical Challenge
Previous Circuits Solutions
Circuit
Solutions in Progress |
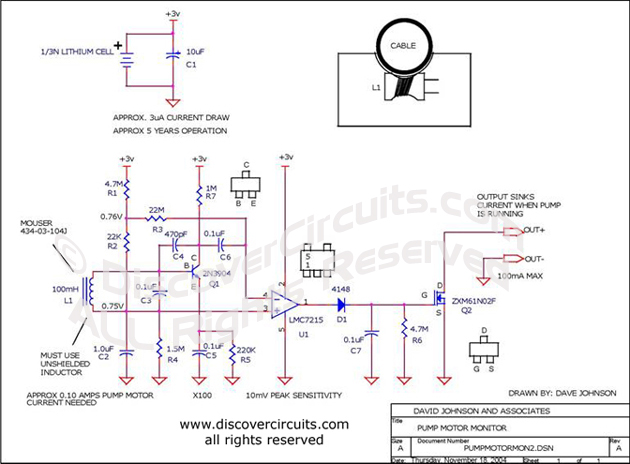
Pump Motor Monitor:
How do you know if an
inaccessible pump motor is turned on, without hiring an electrician to wire in some special
equipment?
The
circuit below solves this problem in a novel way. It clips on the outside of the pump
motorís power cable and provides a transistor switch closure whenever the circuit detects
current flowing to the motor. The circuit draws so little current that a small lithium
cell will power the circuit for years. |
|
 |
|
Background
Several times over the last few years I have received calls from people looking
for a simple circuit that would tell them when a sump pump or water well pump motor was
running. These people told me that the electrical circuits that turn on and off the
motors were frequently inaccessible, often below ground, making it difficult to know if the
motor was running or not. What they wanted was a simple way to let them know when the
motor was on or off, without wiring something into the 120vac or 240vac power supply. At
the time I didnít have a ready circuit for them but I put the requirement into my subconscious
and let my mind work on the problem for a while. After some thought, I came up with the
solution described below. |
How it works
The traditional method for determining if a motor is running or not is to
measure the current flowing through one of the wires supplying power to the motor. When
the motor is off, the current should be near zero and will jump to the running current when
the motor turns on. The classic sensor for measuring AC current is a current
transformer. In a typical AC current transformer configuration, one of the wires
carrying current to the motor would be routed through the transformer. The one wire
forming a single turn primary. The magnetic field produced by the current flowing
through the wire induces a voltage in the secondary winding of the transformer, proportional
to the current. The output voltage of the transformer would then be connected to a
circuit, which would activate a switch, whenever current was drawn by the motor.
However, this single wire connection is often difficult and can be dangerous for a novice to
wire into an electrical system. The installer would have to cut into the power cable to
expose one wire or find an exposed single wire somewhere else, perhaps inside the circuit
breaker box. Clamping a typical current meter, using a current transformer probe, over
the whole power cable will result in a zero current reading, since the field produced by the
return wire, which is also inside the cable, will be canceled by the magnetic field of the
supply wire. So, how do you detect the current? The solution is to rely on the
fact that the two wires carrying current inside the cable are not perfectly in parallel with
each other. A small coil, acting like a transformer, placed against one wire, will pick
up more of its field and less from its neighbor. Although the signal produced by the
coil will be small, enough can be collected to indicate if the motor is drawing current or
not. When connected to a sensitive circuit, a simple monitoring device can be produced.
The user just has to find a suitable place to clamp the box containing the monitoring circuit
to the outside jacket of the power cable, supplying current to the motor. |
| I chose to
power the monitoring circuit with a small battery. With a simple battery supply, there is less
a user has to worry about. Using modern components, I was able to keep the current
consumption to a very low level. A small lithium battery cell will power the circuit for
about 5 years. The two wires connected to the circuitís transistor switch can be used to
turn on a light or noisemaker, located some distance from the monitoring box.
|
| The circuit uses a small
unshielded 100mH inductor as current transformer. The voltage generated by the coil is
fed to a single transistor circuit, which is configured as a high gain, low frequency
amplifier. The circuit has a gain over 100. The output of the amplifier is
connected to a voltage comparator. The DC bias voltages at the input of the comparator
set the sensitivity of the signal from the amplifier at about 10 millivolts. This should
be sufficient for most applications. If the coil is placed properly against the outside
of the power cable, a current of 100ma AC should be sufficient to activate the circuit.
The output of the comparator is a pulse train equal to the 50Hz or 60Hz power line frequency.
A simple diode rectifies the pulses and produces sufficient DC voltage to turn on the
transistor Q2. The transistor acts as a switch, which closes when the circuit detects
motor current flowing through the power cable. |
| If
the user wishes to power an indicator light from the same 3 volt battery, he should use a
flashing LED circuit, such as xyz. This type of circuit will not tax a small battery.
Of course, the user can increase the battery size. The circuit will work fine from two
1.5 volt AA cells.
|
|